Code
I created and maintain several open-source Python packages for my research, and I hope they will also be useful for others.
Why?
Open source scientific code plays a vital role in advancing research and promoting transparency in the scientific community. By making code freely available to the public, researchers foster collaboration, reproducibility, and innovation. Open source code allows others to validate and build upon existing work, accelerating the pace of scientific discovery and promoting reliable scientific results. Overall, I believe open source scientific code promotes a culture of openness, collaboration, and integrity, driving scientific progress forward and benefiting the global research community as a whole.
gyptis
Computational Photonics in Python with the finite element method.
Documentation and examples can be found on the website gyptis.gitlab.io

nannos
Fourier Modal Method for multilayer metamaterials with automatic differentiation.
Documentation and examples can be found on the website nannos.gitlab.io

protis
Plane wave expansion method for photonic crystals with automatic differentiation.
Documentation and examples can be found on the website protis.gitlab.io
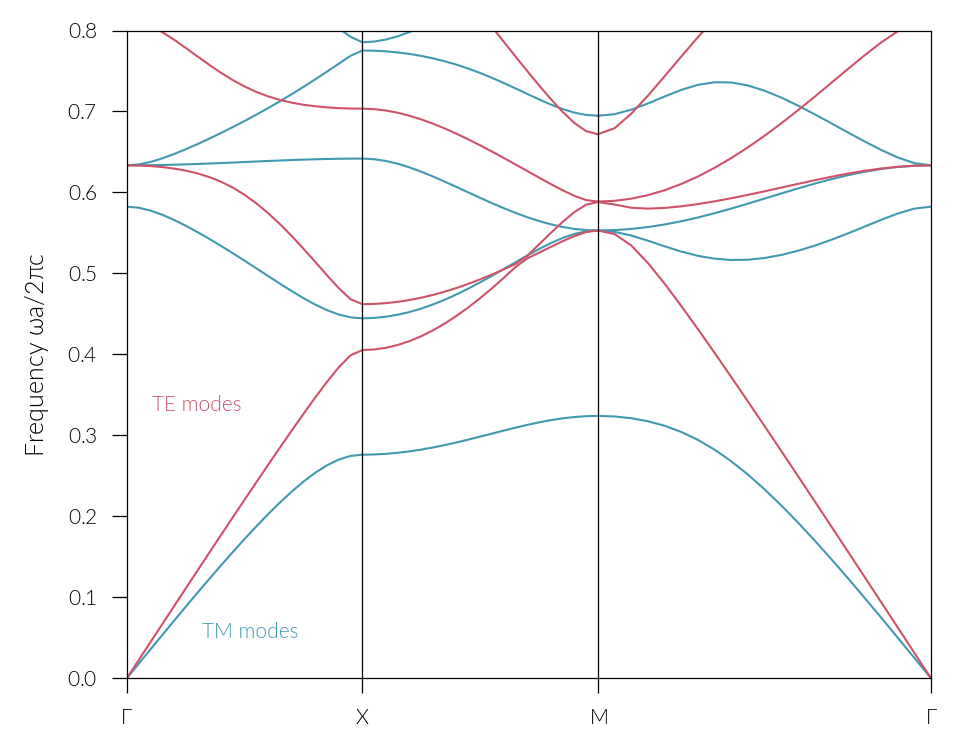
pytmod
(Eigen)Solver for photonic slabs with permittivity modulated periodically in time.
Documentation and examples can be found on the website bvial.info/pytmod
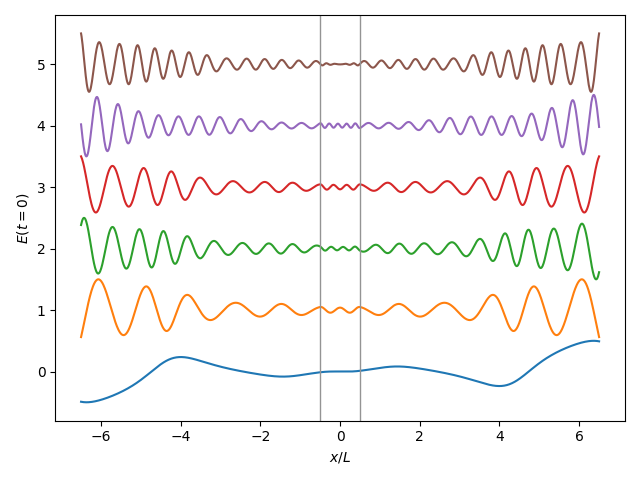
pylatt
Phononic lattices in Python.

klove
Elastic plates.

ashx
FEniCSx tools.
geolia
Geometry and mesh tools.

refidx
Python package to retrieve the refractive index of material from the refractiveindex.info database.
Documentation and examples can be found on the website benvial.gitlab.io/refidx

coaxtract
Permittivity extraction for multilayer stacks using an open-ended coaxial probe.
Documentation and examples can be found on the website benvial.gitlab.io/coaxtract

cpwxtract
Tools for extracting material properties from coplanar waveguide measurements.
Documentation and examples can be found on the website benvial.gitlab.io/cpwxtract

tdsxtract
Tools for material parameters extraction from THz time domain spectroscopy measurements.
Documentation and examples can be found on the website tdsxtract.github.io/tdsxtract