Topology Optimization
I am interested in optimizing the shape of photonic and microwave devices for various applications and control of electromagnetic waves.
Open-Source Inverse Photonic Design
In recent years, technological advances in nanofabrication have opened up new applications in the field of nanophotonics. To engineer and develop novel functionalities, rigorous and efficient numerical methods are required. In parallel, tremendous advances in algorithmic differentiation, in part pushed by the intensive development of machine learning and artificial intelligence, has made possible large-scale optimization of devices with a few extra modifications of the underlying code. We present here our development of three different software libraries for solving Maxwell’s equations in various contexts: a finite element code with a high-level interface for problems commonly encountered in photonics, an implementation of the Fourier modal method for multilayered bi-periodic metasurfaces and a plane wave expansion method for the calculation of band diagrams in two-dimensional photonic crystals. All of them are endowed with automatic differentiation capabilities and we present typical inverse design examples.
Related article
- B. Vial, and Y. Hao, Open-Source Computational Photonics with Auto Differentiable Topology Optimization. Mathematics 10 (20), (2022) DOI | URL
Related code
- B. Vial, gyptis: Computational Photonics in Python with the finite element method (2020). gitlab
- B. Vial, nannos: Fourier Modal Method for multilayer metamaterials with automatic differentiation (2021). gitlab
- B. Vial, protis: Plane wave expansion method for photonic crystals with automatic differentiation (2021). gitlab
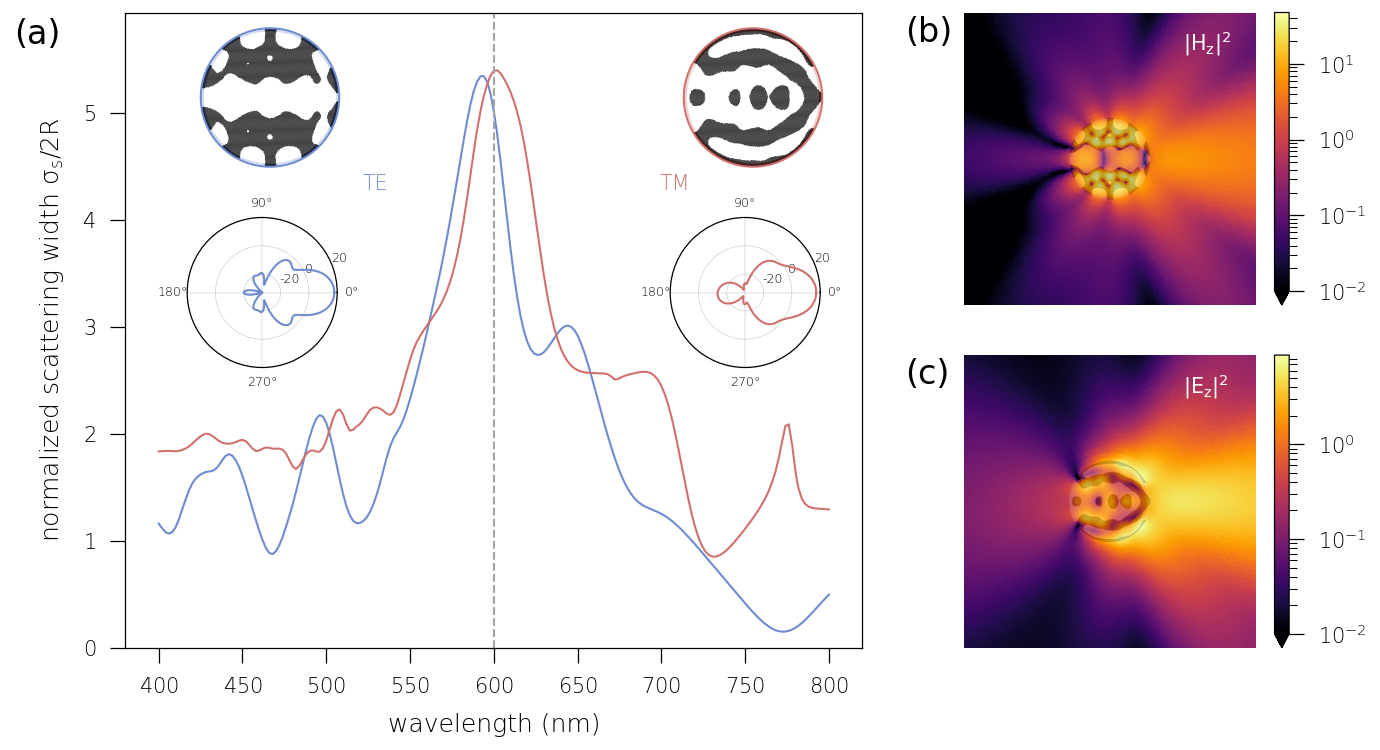
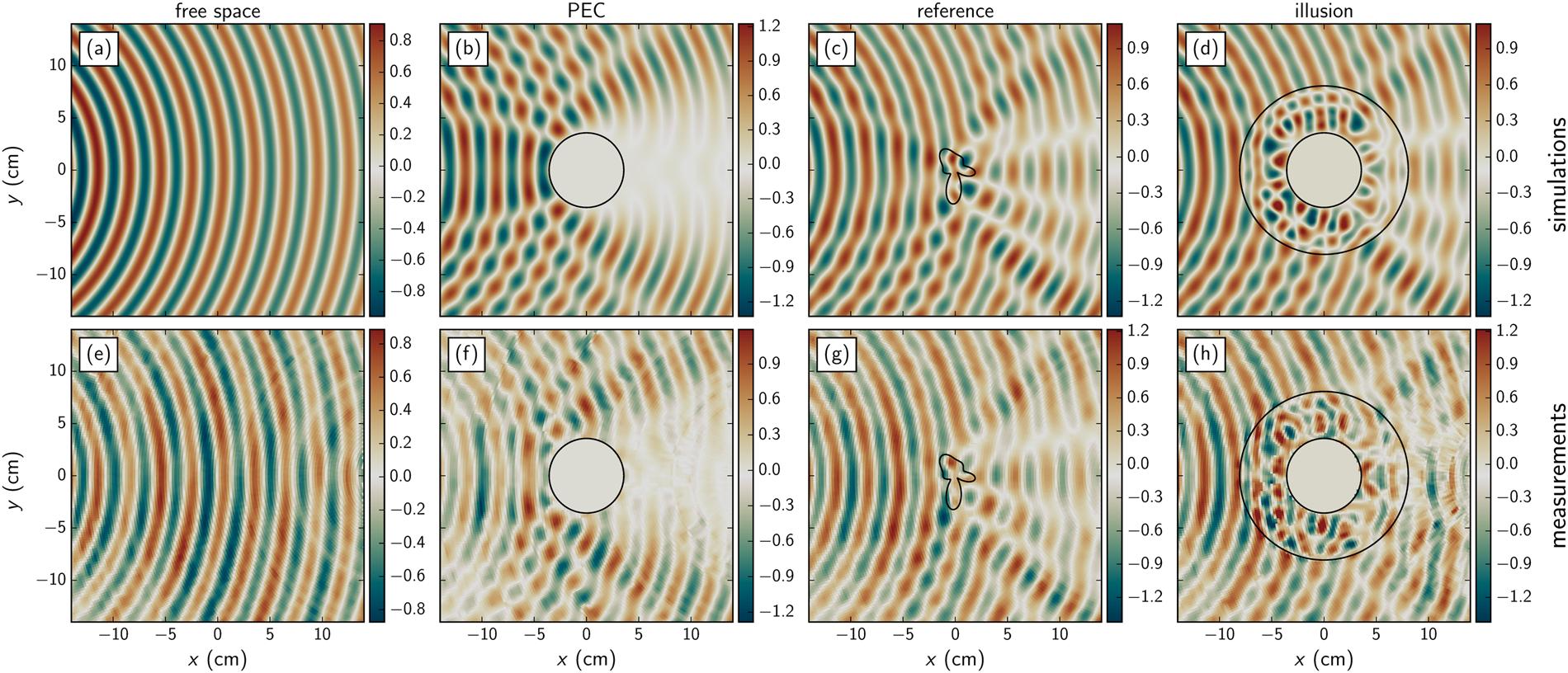
Illusion device
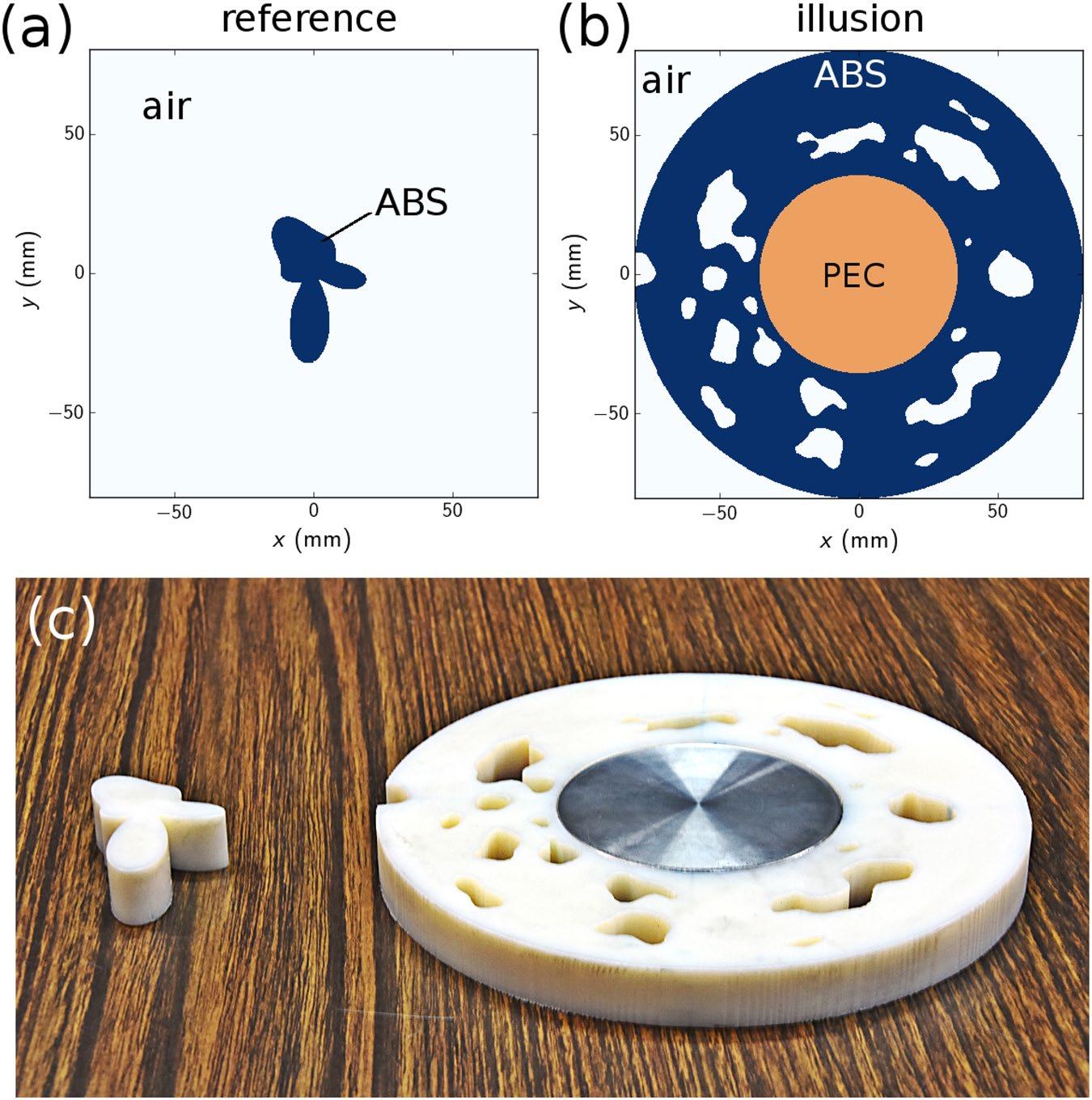
We report the design, fabrication and experimental verification of an illusion device working at microwave frequencies. A two dimensional topology optimization procedure is employed to find the binary layout of a dielectric coating that, when wrapped around a metallic cylinder, mimics the scattering from a predefined, arbitrarily-shaped dielectric object. Fabrication is carried out with 3D-printing and spatially resolved near field measurements in a waveguide configuration were performed, allowing us to map the illusion effect. Our work provides general guidelines for engineering electromagnetic illusions but can be extended to shape the near and far-field radiations using low index isotropic materials.
Related article
Invisibility cloaking
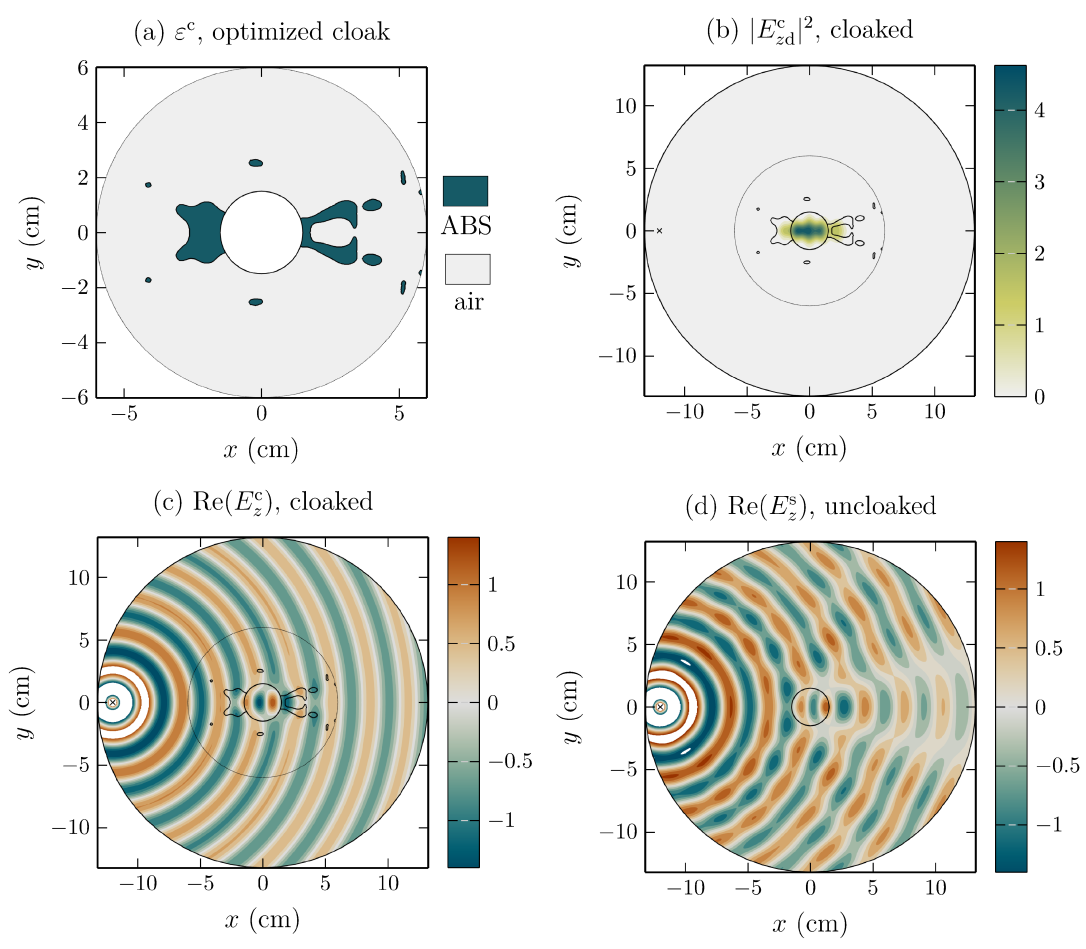
I designed an all-dielectric cloaking device at microwave frequencies. A gradient based topology optimization is employed to find a dielectric permittivity distribution that minimizes the diffracted field in free space. The layout is binary, i.e. made either of standard ABS plastic or air and is designed to reduce the scattering from an ABS cylinder excited by a line source for TE polarization. We study the performances of cloaks optimized for one, two and three frequencies in terms of scattering reduction and correlations with respect to the free space propagation case. Finally, a modal analysis is carried out providing physical insights on the resonant cloaking mechanism at stake.